
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/Protein_primary_structure.svg/2000px-Protein_primary_structure.svg.png
2. The mutation that had the most effect to the protein is frameshift mutation because it involves insertion and deletion that has a great effect to the amino acids. When the DNA inserted another base, the amino acids changed into different amino acids. When the DNA deleted a base, the amino acids started twice. The weakest mutation is substitution because it only substitutes a base for another and does not effect the amino acids much as most of the proteins still were the same from the original amino acid sequence.
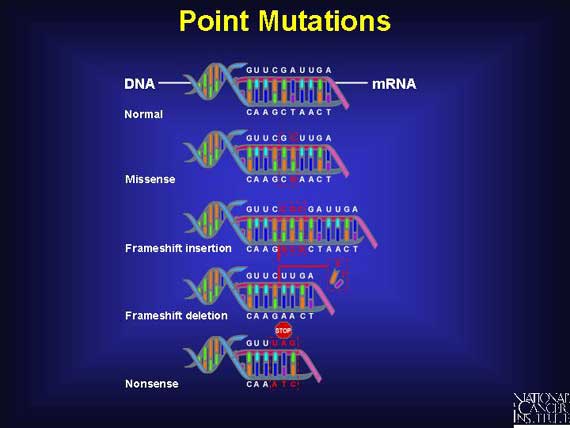
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b1/Point_Mutation.jpg
3. In step 7, I chose insertion because it's a harmful mutation. Insertion is more effective to the amino acids than deletion and substitution because more amino acids turn into different amino acids than deletion and substitution. It matters where the mutation occurs because has to occur between the codons.
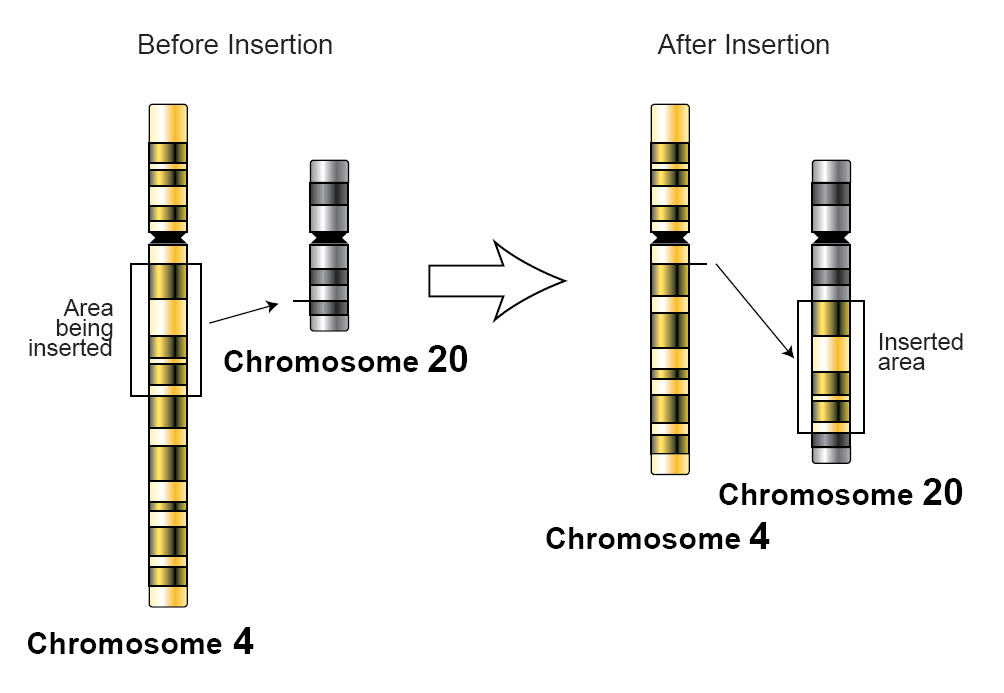
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/06/Insertion-genetics.png
4. Mutations can affect our life by causing proteins to not work properly and can cause disorders in the body.
Conditional Mutations:
A type of mutation that affects the phenotype by temperature.
http://www.nature.com/scitable/content/5140/10[1].1038_ncb437-f2_full.jpg
No comments:
Post a Comment