We learned about our genetic code. We learned about the structure of our code which includes a double helix which is two strands twisted around each other and is made of nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three parts, an anitrogen base, a phosphate group and a sugar. In our genetic code, our DNA is antiparallel which is when each nucleotide bonds with another nucleotide. Also our code is made of nitrogen bases that includes purines and pyrimidines. We learned about our DNA. It includes semi conservative DNA replication. It includes many steps that includes unzipping and zipping. The result of this is getting 2 identical strands. We learned that the base pair rules are A=U, C=G, T=A.
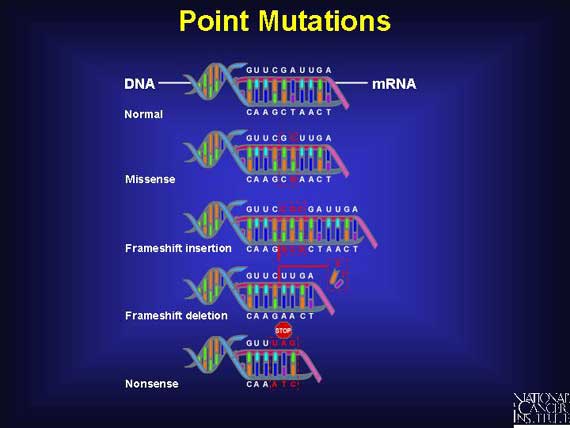
We learned about RNA and DNA and its structural differences like being single stranded, having rbose and containing uracil. The function of RNA is that it serves as a temporary copy of a gene , delivers the copy to the ribosomes, and ribosomes would use the copy to make proteins. We learned about transcription and translation. Transcription is a process where RNA polymerase reads and copies DNA code for the messenger RNA. Translation is when the messenger RNA arrives at the ribosome and is read 3 bases at a time and turned into protein. The result of this is that a long chain of amino acids are made and chains of amino acids twist, folds and combines with other chains. We learned about the types of mutations . It includes point mutation where a change in one or two base paris of DNA, very small and are very common. It also includes frameshift mutation, Substitution , insertion and deletion. Frameshift mutation is a mutation that includes insertion and deletion. Insertion is when an extra base pair is added to the code. Deletion is when a base pair is left out of the code.
Lastly, we learned about gene expression and regulation. We learned that gene regulation is cells that don't want to waste energy or over express genes and have a variety of steps used to control the expression of a single gene. We learned about eukaryotic regulation. It's more complex that bacterial regulation and proteins will bind before a gene and are required for the gene to be expressed.
We learned about RNA and DNA and its structural differences like being single stranded, having rbose and containing uracil. The function of RNA is that it serves as a temporary copy of a gene , delivers the copy to the ribosomes, and ribosomes would use the copy to make proteins. We learned about transcription and translation. Transcription is a process where RNA polymerase reads and copies DNA code for the messenger RNA. Translation is when the messenger RNA arrives at the ribosome and is read 3 bases at a time and turned into protein. The result of this is that a long chain of amino acids are made and chains of amino acids twist, folds and combines with other chains. We learned about the types of mutations . It includes point mutation where a change in one or two base paris of DNA, very small and are very common. It also includes frameshift mutation, Substitution , insertion and deletion. Frameshift mutation is a mutation that includes insertion and deletion. Insertion is when an extra base pair is added to the code. Deletion is when a base pair is left out of the code.
Lastly, we learned about gene expression and regulation. We learned that gene regulation is cells that don't want to waste energy or over express genes and have a variety of steps used to control the expression of a single gene. We learned about eukaryotic regulation. It's more complex that bacterial regulation and proteins will bind before a gene and are required for the gene to be expressed.